Minions
Welcome to the Minions Page
Overview
This page is where you will manage your minions and put them into Target groups.The Minions workspace is used to:
- View minion details
- Run ad-hoc jobs or commands
- Create and save new targets
- Adjust target settings, such as attached pillars
- Search for a minion or sort minions based on their minion ID or other system properties (referred to as grains)
- Managing minions and targets
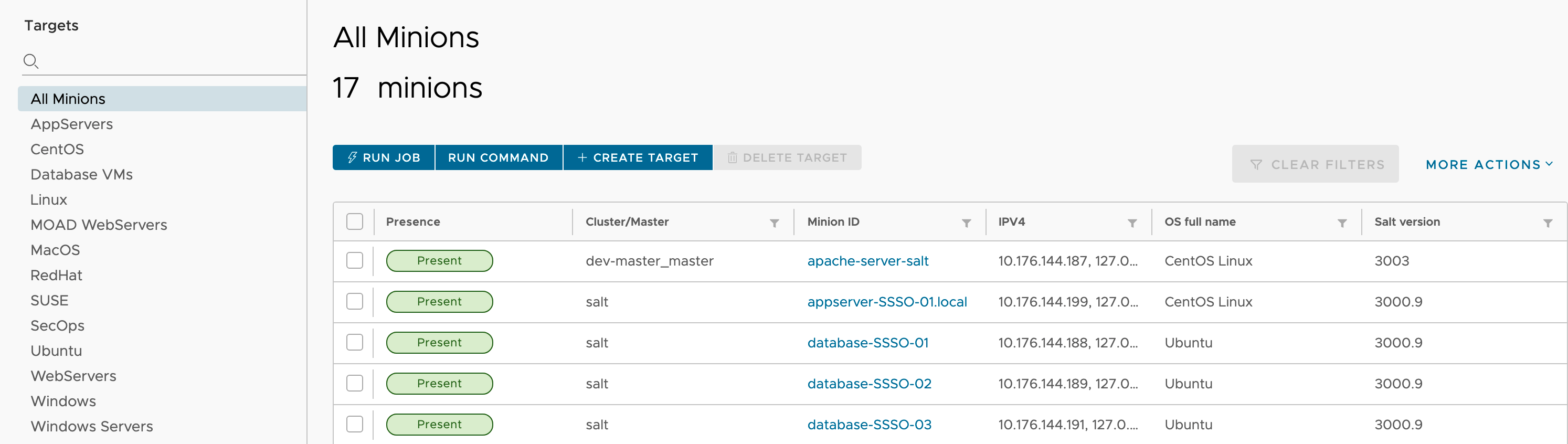
The Minions workspace includes a list of all Salt minions that are running the minion service and that are currently managed by SaltStack Config. Minions are nodes running the minion service, which can listen to commands from a Salt controller and perform the requested tasks. Salt Masters can themselves run the minion service, which makes it possible to configure and manage the node running the Salt controller service as needed. A good example of treating the Salt Master like a minion could be something like pushing config files down to the master.d directory.
The side panel of the workspace includes a list of targets. A target is the group of minions, across one or many Salt controllers, that a job’s Salt command applies to. A Salt controller can also be managed like a minion and can be a target if it is running the minion service. Defining a target for a job or operation also prevents the operation from running on nodes that should not run that operation. Targets can contain minions that are connected to any Salt controller in your environment. You can attach pillar data to different targets. Pillars are structures of data defined on the Salt controller and passed through to one or more minions, using targets. They allow confidential, targeted data to be securely sent only to the relevant minion.
By default, when you open the workspace, the All Minions target is active. The All Minions target lists all the minions you have permission to access.
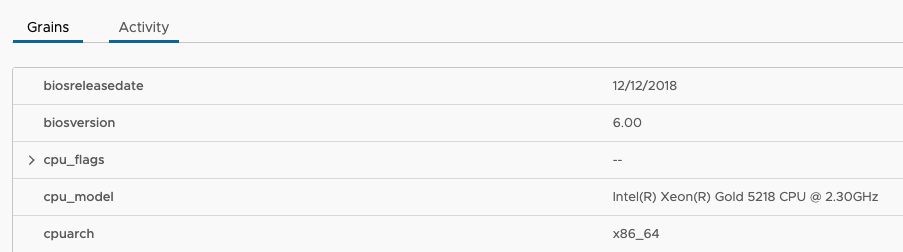
Grains
When you click on a minion you will see a tab called grains. Salt comes with a system to gather and present data about the minion, this is called grains. Grains are essentially metadata about the minion, like OS Type, FQDN, and much more. Admins can use these grains gather information about a minion and include that data in state files, or use it to Target minions.
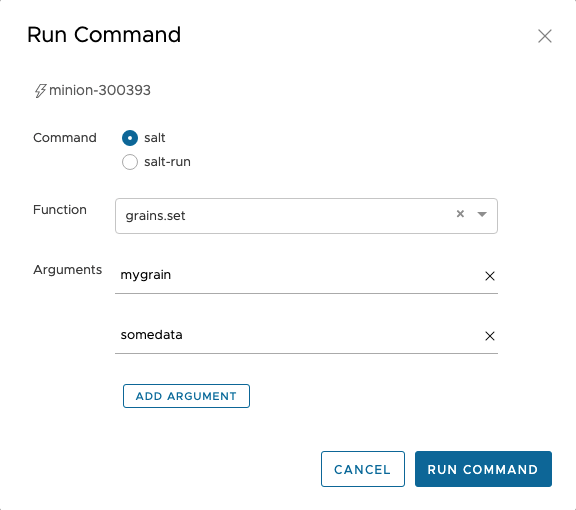
Admins can also create custom grains via SaltStack Config UI or via the CLI. From within SaltStack Config you can click on a minion and click “Run Command” then choose the function grains.set and then add your key:value arguments.
Once you do this the grain will show up in the list, then this grain can be used for targeting and filtering via jinja etc.
Using Grains with States
Grains are available to states via the grains dictionary and can be called in the state file.
{{ grains[‘os.family’] }}
The grains.get function can be used to go deeper into the grains.
{{ salt['grains.get']('os', 'Debian') }}
Note: The salt command before the grain.get just tells the system to use the grains state module. This is explained in more detail in the File Server States sections.
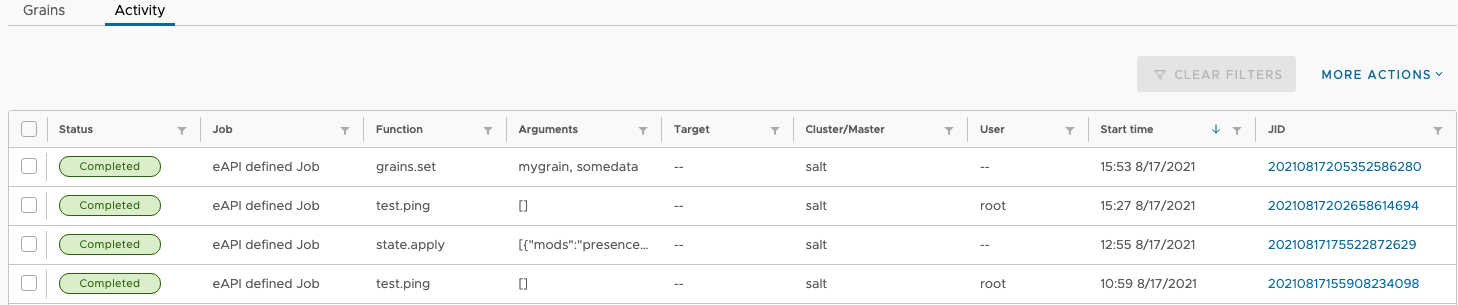
Activity Section
The other tab you will see available when clicking on a minion is the Activity Tab. This tab provides visibility into jobs that are running or have run against the minion. Admins can also see all activity across all minion in the Config–>Activity section, but there may be cases where just looking at the activity of a single minion can be helpful.